
This extra support gives the membrane increased strength and resilience to withstand reprobing and autoclaving (121℃) while maintaining the ease of wetting of nitrocellulose. Supported nitrocellulose is an inert support structure with nitrocellulose applied to it. Unsupported nitrocellulose is innately fragile and are not recommended for stripping and reprobing.
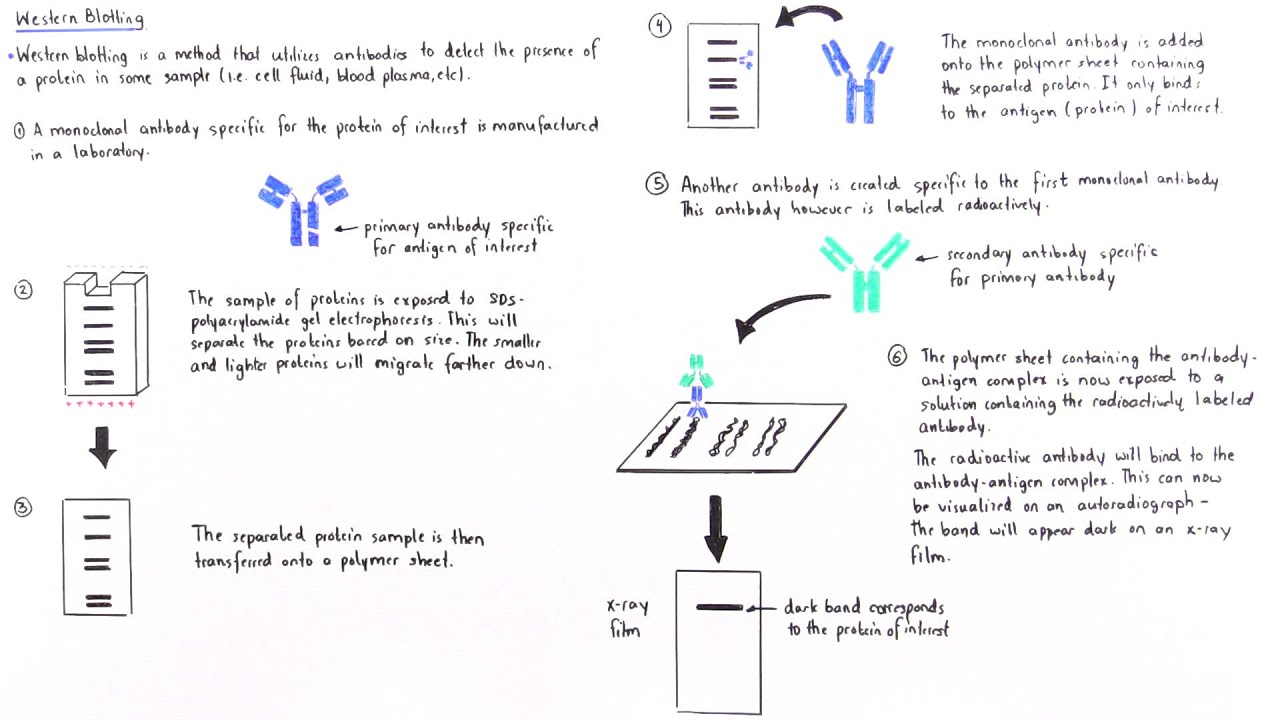
Nitrocellulose membranes are easily wetted in water or transfer buffer, and it is compatible with a wide range of protein detection systems. Nitrocellulose and Supported Nitrocellulose But alcohol may cause a reduction in the gel pore size, precipitation of some proteins, and some basic proteins to become positively charged or neutral.Ĭonsiderations for Selecting Nitrocellulose or PVDF to use for Western Blots However, SDS in the transfer buffer decreases the binding efficiency of protein to nitrocellulose membrane PVDF membrane can be substituted if desired.Īlcohol, on the other hand, removes the SDS from SDS-protein complexes and improves the binding of protein to nitrocellulose membrane. SDS promotes elution of the protein from the gel and in cases where certain proteins are difficult to elute from the gel, SDS may be added to the transfer buffer. SDS and alcohol play opposing roles in a transfer. Use acid-gel transfer protocol (membrane toward cathode) Tank blotting recommended temperature regulation may be needed to maintain activity Tank blotting recommended needs high-capacity, small pore-size membrane pH of buffer may be criticalĭepends on pH of gel buffer and pI of protein of interest Towbin with or without SDS, CAPS, carbonate, Bjerrum Schafer-Nielsen Compatible Transfer Buffer by Gel Type Gel Type In addition, alcohol (methanol or ethanol) may be included in the transfer buffer to promote binding of proteins to membranes, and SDS may be added to promote elution of proteins from gels. Transfer buffers contain a conductive, strong buffering agent (for example, Tris, CAPS, or carbonate) in order to maintain the conductivity and pH of the system during transfer. Preinstalled, customizable programs for transfers of most proteins, user-programmable settings for traditional semi-dry techniquesĬooling with ice pack or refrigerated water recirculator Power and transfer time limited due to lack of cooling options Widest range of power settings and transfer times Comparison of Western Blotting Transfer Systems Filter papers and membranes are pre-wet and packaged in single-use packages, simplifying assembly of the transfer stack. Transfer conditions must be optimized for proteins of different molecular weights, e.g., to prevent under-transfer (incomplete transfer of proteins out of the gel) or over-transfer (loss of proteins passing completely through the membrane).Ī recent development, these systems utilize specialized apparatus that use proprietary filter papers and specialized buffers to rapidly and efficiently transfer proteins. Both the voltage and the distance between the electrodes then play a major role in governing the rate of elution of the proteins from the gel. The electric field strength (measured in V/cm) that is generated between the electrodes is the driving force for transfer. Voltage is applied between the electrodes and proteins migrate to the membrane following the current that is generated by the applied voltage across the electrodes. During this process, the membrane and gel are placed together, with filter paper between two electrodes. The most common method of transfer in western blotting is electrophoretic transfer, where an electric field is used to elute proteins from gels and transfer them to membranes. Gel and Membrane Setup for Electrophoretic Transfer


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
